A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z
| Sr. | Term | Definition |
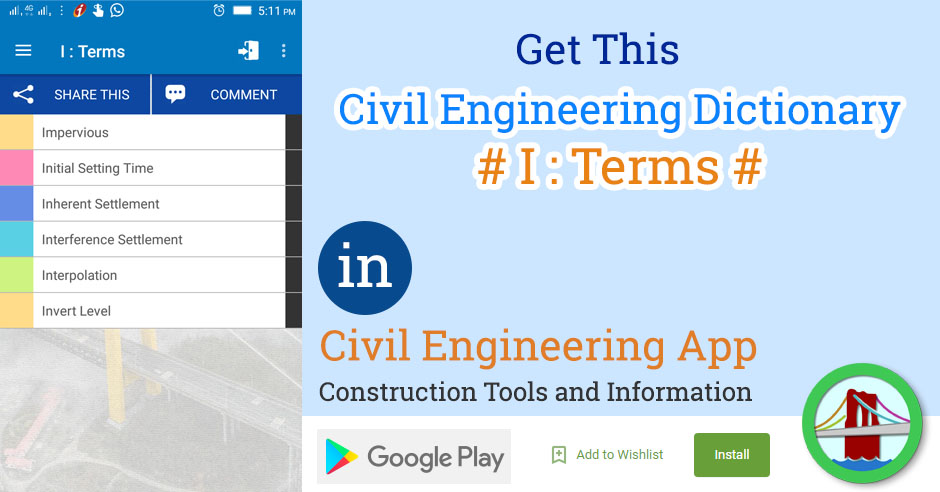
| 1 | Impervious | Resistant to movement of water; a description of relatively waterproof soils such as clays through which water percolates at about one millionth of the speed with which it passes through gravel. |
| 2 | Initial Setting Time | The time required before a concrete mix can carry a small load without sinking like a mud. This is after about one hour in warm weather. |
| 3 | Inherent Settlement | The sinking of a foundation due only to the loads which it puts on the soil below it and not to the loads on any nearby foundations. In city sites where the foundations are on clay, all foundations suffer both inherent and interference settlement. |
| 4 | Interference Settlement | The sinking of a foundation due to loads on foundations near it and the natural extension of their settlement craters beyond their own boundaries. |
| 5 | Interpolation | (1) Inferring the position of a point between known points on a graph by assuming that the variation between them is smooth. Usually the assumption is that the variation is linear (A straight-line variation). (2) To estimate untested values which fall between tested values. |
| 6 | Invert Level | The level of the lowest part of a pipe invert. |
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z